Understanding Meniscus Tears
The meniscus is a C-shaped piece of cartilage that acts as a shock absorber between your thighbone (femur) and shinbone (tibia). It helps to distribute weight evenly across the knee joint, allowing for smooth and stable movement. A meniscus tear occurs when this cartilage is torn, usually due to a sudden twisting or impact injury.
Anatomy and Function of the Meniscus
The meniscus is made of tough, rubbery cartilage that helps to cushion the knee joint. It also plays a crucial role in stabilizing the knee and providing lubrication. There are two menisci in each knee: the medial meniscus (on the inside of the knee) and the lateral meniscus (on the outside of the knee).
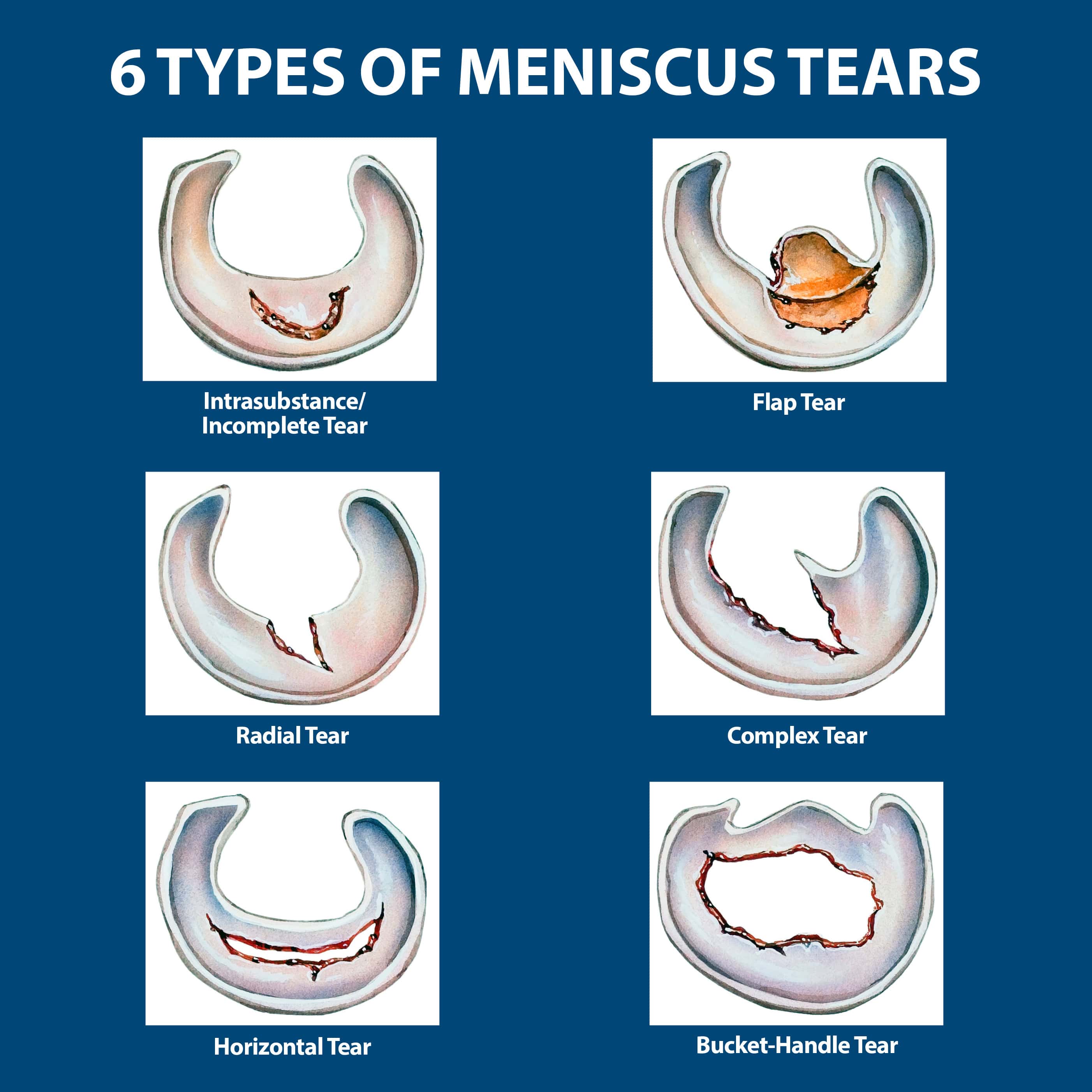
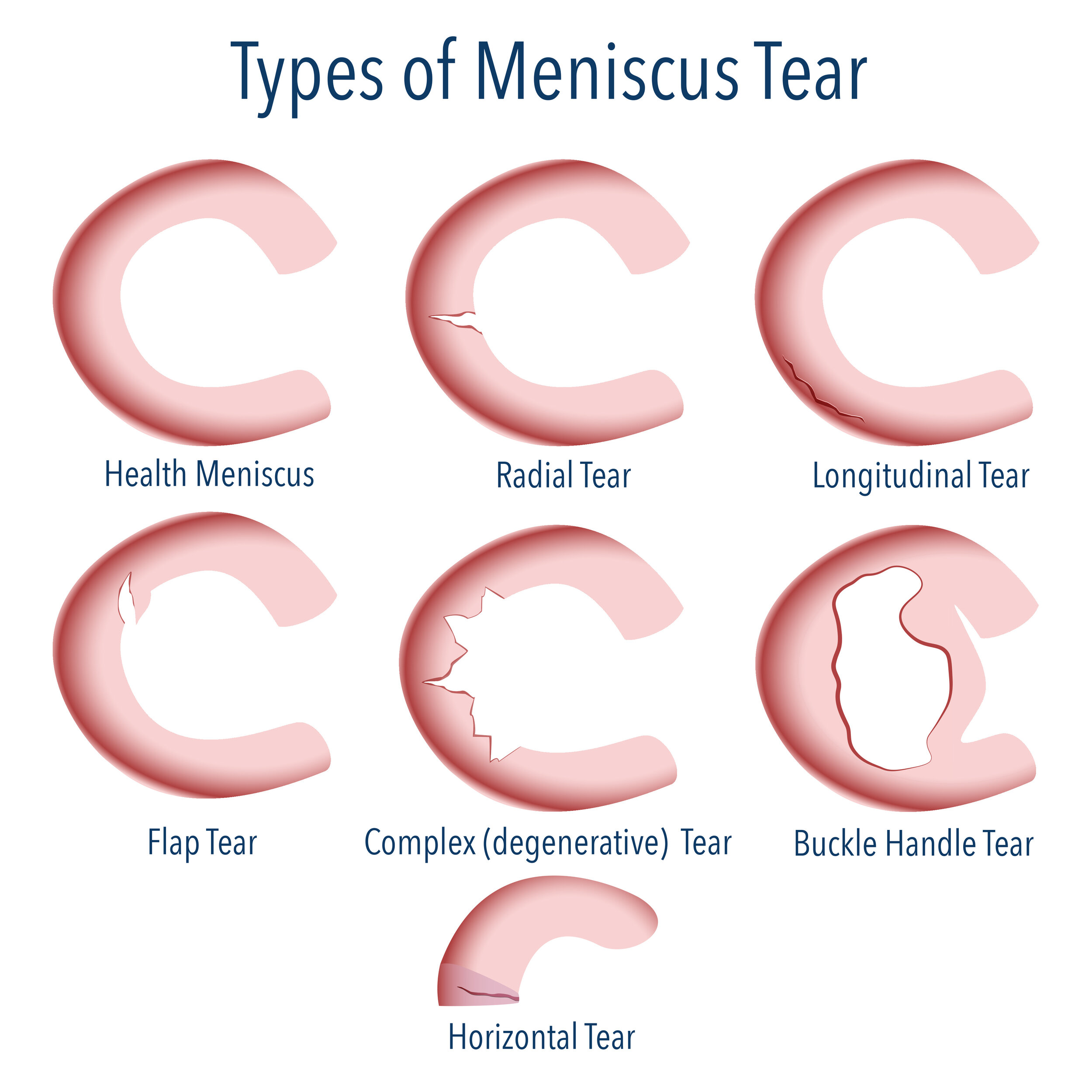
Types of Meniscus Tears
Meniscus tears can be classified based on their location and severity. The most common types of meniscus tears include:
- Horizontal Tear: A horizontal tear runs across the width of the meniscus, often occurring with other types of tears.
- Radial Tear: This type of tear runs from the outer edge of the meniscus towards the center.
- Oblique Tear: An oblique tear occurs at an angle, often involving the outer edge of the meniscus.
- Flapper Tear: A flapper tear is a more severe type of tear where a portion of the meniscus is completely detached.
Causes of Meniscus Tears
Meniscus tears are common injuries, particularly among athletes. Some of the most common causes include:
- Sports Injuries: Activities that involve twisting, pivoting, or sudden impact, such as football, basketball, and skiing, can increase the risk of a meniscus tear.
- Age-Related Degeneration: As we age, the meniscus can become thinner and weaker, making it more susceptible to tears.
- Trauma: A direct blow to the knee or a sudden fall can cause a meniscus tear.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
A meniscus tear can cause a range of symptoms, depending on the severity of the tear and the location of the injury. Some people experience only mild discomfort, while others may have significant pain and difficulty walking.
Understanding the signs and symptoms of a meniscus tear is crucial for prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Early diagnosis can help prevent further damage and improve the chances of a successful recovery.
Symptoms of a Meniscus Tear
The following are some common symptoms of a meniscus tear:
- Pain: Pain is the most common symptom of a meniscus tear. The pain is usually located in the knee joint and may worsen with activity, especially twisting or bending the knee.
- Swelling: Swelling around the knee joint is another common symptom. It may develop immediately after the injury or gradually over a few days.
- Locking: The knee may lock or catch, making it difficult to straighten or bend. This happens when a piece of torn meniscus gets stuck in the joint.
- Instability: The knee may feel unstable or give way, especially during activities that involve twisting or pivoting.
- Stiffness: The knee may feel stiff and difficult to move, especially after periods of inactivity.
- Clicking or popping: Some people may hear a clicking or popping sound in the knee when they move it.
Diagnosis of a Meniscus Tear
Diagnosing a meniscus tear usually involves a combination of physical examination, imaging tests, and sometimes arthroscopy.
Physical Examination
A doctor will perform a physical examination to assess the range of motion in your knee, check for tenderness, and evaluate your ability to walk and perform other activities. They will also ask you about your symptoms and the mechanism of injury.
Imaging Tests
Imaging tests, such as an MRI, can help confirm the diagnosis and determine the severity of the tear. An MRI provides detailed images of the knee joint, allowing the doctor to visualize the meniscus and any tears.
Arthroscopy
Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that allows the doctor to directly visualize the inside of the knee joint. It is often used to confirm the diagnosis, assess the severity of the tear, and perform any necessary repairs.
Comparing Symptoms of a Meniscus Tear with Other Knee Injuries
It’s important to note that the symptoms of a meniscus tear can be similar to those of other knee injuries, such as ligament sprains, cartilage damage, and arthritis. A thorough examination and imaging tests are necessary to determine the underlying cause of the symptoms.
| Symptom | Meniscus Tear | Ligament Sprain | Cartilage Damage | Arthritis |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pain | Yes, often worse with activity | Yes, often worse with weight-bearing | Yes, often worse with activity | Yes, often worse with activity and in the morning |
| Swelling | Yes, may be gradual or immediate | Yes, often immediate | Yes, may be gradual or immediate | Yes, often gradual |
| Locking | Yes, due to trapped meniscus fragment | No | No | No |
| Instability | Yes, may feel like giving way | Yes, may feel like giving way | Yes, may feel like giving way | Yes, may feel like giving way |
| Stiffness | Yes, especially after inactivity | Yes, especially after inactivity | Yes, especially after inactivity | Yes, especially after inactivity |
| Clicking or popping | Yes, may be present | No | No | No |
Treatment Options: Meniscus Tear
The treatment approach for a meniscus tear depends on various factors, including the severity of the tear, your age, activity level, and overall health. The goal of treatment is to relieve pain, improve function, and prevent further damage to the knee.
Conservative Treatment
Conservative treatment options are typically the first line of approach for meniscus tears, especially for less severe tears or those in individuals with low activity levels. These methods aim to reduce pain and inflammation, allowing the knee to heal naturally.
- Rest: Avoid activities that put stress on the knee, such as running, jumping, or squatting.
- Ice: Apply ice packs to the affected area for 15-20 minutes at a time, several times a day, to reduce swelling and inflammation.
- Compression: Use a compression bandage to reduce swelling and provide support to the knee.
- Elevation: Keep the injured leg elevated above heart level to reduce swelling.
- Pain Medication: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or naproxen, can help manage pain and inflammation. In some cases, your doctor may prescribe stronger pain medications.
- Physical Therapy: A physical therapist can teach you exercises to strengthen the muscles around the knee, improve flexibility, and restore range of motion. This can help you regain stability and function in your knee.
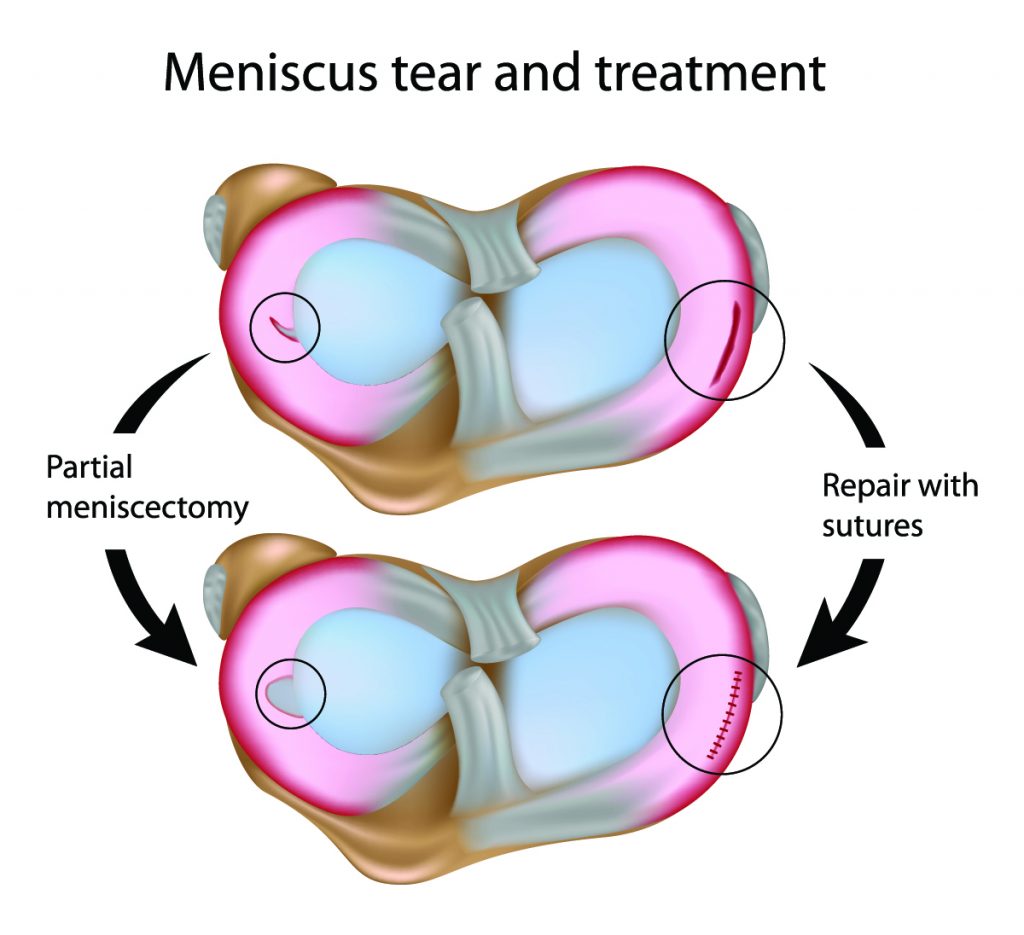
Surgical Treatment
If conservative treatment fails to provide relief or if the tear is severe, surgery may be recommended. Surgical procedures for meniscus tears typically involve arthroscopic surgery, a minimally invasive technique.
- Arthroscopic Surgery: This procedure involves making small incisions in the knee and inserting a thin, telescope-like instrument called an arthroscope. The arthroscope allows the surgeon to visualize the inside of the knee and repair or remove the torn meniscus.
- Meniscus Repair: In this procedure, the surgeon stitches the torn meniscus back together. This is usually an option for younger individuals with a stable tear and good blood supply to the meniscus.
- Meniscectomy: This procedure involves removing the damaged portion of the meniscus. It is often performed for older individuals or those with tears that are not repairable.
Comparing Treatment Options
The choice between conservative and surgical treatment depends on several factors, including:
| Factor | Conservative Treatment | Surgical Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Age | Often preferred for older individuals with less active lifestyles. | May be more suitable for younger individuals with more active lifestyles. |
| Activity Level | May be sufficient for individuals with low activity levels. | May be necessary for individuals with high activity levels who need to regain full function. |
| Severity of Tear | Suitable for less severe tears. | May be necessary for severe tears that are not healing or causing significant pain. |
| Overall Health | A good option for individuals with underlying health conditions. | May not be suitable for individuals with certain health conditions. |
A meniscus tear is a common injury, especially for athletes. It’s like a shock absorber in your knee, and when it’s torn, it can really mess things up. Just ask JJ McCarthy, the Michigan quarterback who had to undergo knee surgery after tearing his meniscus.
It’s a tough injury, but with proper treatment and rehab, you can get back to doing what you love.
A meniscus tear can sideline you for a while, just like a bad game for the minnesota vikings can ruin a season. But just like a dedicated athlete, with proper rehab, you can bounce back stronger and more resilient.
A meniscus tear is a tough injury, but with the right treatment, you’ll be back on your feet in no time.
